When internet has changed our life in almost every segment, it's probably even changed how we search for information and also address solutions about our health problems. Healthcare landscape has evolved keeping up with the digital demand and now telemedicine is having its moment.

During the COVID-19 pandemic, telemedicine played a pivotal role providing remote healthcare access. It not only reduced the burden on healthcare systems, but also ensured the safety and well-being of patients and healthcare providers. Telemedicine drive during this period resulted in raised awareness of this domain, making it a well-known and accepted mode of healthcare delivery.
Telemedicine is not a replacement for all in-person care. This article is not about influencing your thoughts and make you believe otherwise. It is no brainer to assume that not every type of visit is possible remotely. You still have to go into the clinic for things like imaging tests and blood work, as well as for diagnoses that require a more hands-on approach.
All that said, Telemedicine will remain the integral part of the healthcare ecosystem as Convenience is a valuable factor in many scenarios.
This article will walk you through the telemedicine eco-system, pointing out how different segments of your healthcare organization needs to be aligned in a thoughtful and strategic manner to maximize the potential of your telemedicine application.
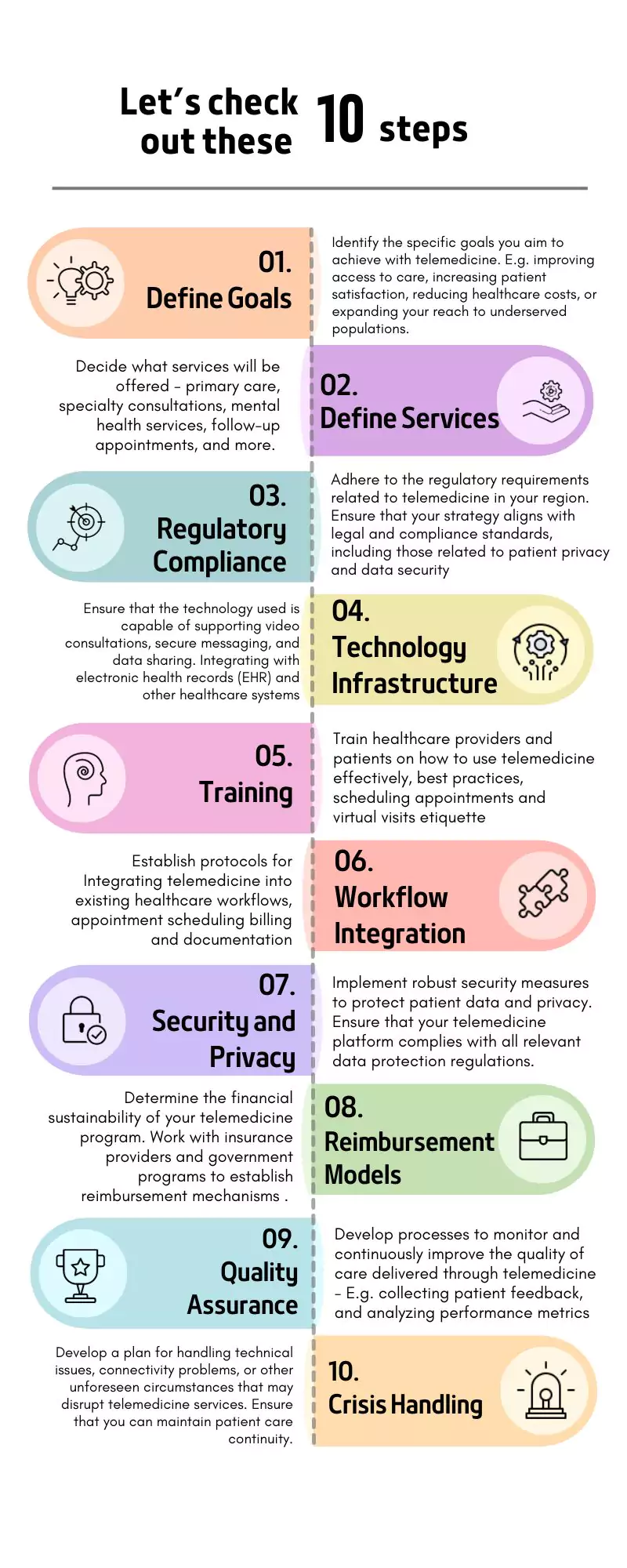
Certainly, defining objectives and goals in your telemedicine strategy is a critical step in ensuring that your telemedicine program aligns with your organization's mission and meets the specific needs of your patients and stakeholders.
Start by defining clear and specific objectives for your telemedicine program. Objectives should be measurable and time-bound. For example, you might set a goal to increase the number of telemedicine appointments by a certain percentage within a year.
Other criteria could be improving access to care, increasing patient satisfaction, reducing healthcare costs, or expanding your reach to underserved populations.
If one of your objectives is to improve access to healthcare services, define the specific populations or geographic areas you aim to reach. For example, you might target underserved rural communities or patients with limited mobility.
Similarly, if the objective is cost-efficiency and sustainability, then define goals related to cost savings or cost-effectiveness such as reducing the cost of care delivery and improve resource allocation.
Once you have defined your objectives for telemedicine adoption, next step would be to define the range and nature of services you plan to offer through telemedicine.
| Service Scope | What Questions to ask |
|---|---|
|
Service Types |
What type of specific services you plan to provide through telemedicine? Primary Care or specialty consultations (e.g., cardiology, dermatology, gastroenterology), mental health services, chronic disease management or post-operative follow-ups and preventive care. |
|
Target patient population |
What specific demographics, such as adults, children, elderly individuals, or underserved communities will be focused? Hint: Tailor your services to meet the needs of these populations. |
|
Geographic Reach |
Will it serve patients within your local area, your state, or on a national level? Hint: Assess the licensing and regulatory requirements for offering services across state your country. |
|
Telemedicine Methods |
What kind of modes will be used to conduct telemedicine procedure? This may include real-time video consultations, store-and-forward (asynchronous) telemedicine for sharing medical images and records, and remote patient monitoring with wearable devices. |
|
Cultural and Linguistic Considerations |
Identify if there is diverse cultural backgrounds and languages of patients and healthcare providers involved in telemedicine services that needs to be addressed? Healthcare providers involved in telemedicine will need to understand and respect the cultural norms, values, beliefs, and practices of their diverse patient population. This is important to promote effective communication and ensures that care is delivered with sensitivity to cultural differences. |
In addition, telemedicine platforms should support multiple languages to accommodate patients who are more comfortable communicating in languages other than the primary language of the healthcare provider. This can include offering interpretation services, multilingual interfaces, or access to qualified interpreters during virtual visits.
It is crucial to ensure that healthcare services delivered via telemedicine adhere to legal and regulatory requirements.
| Compliance | Requirements to adhere |
|---|---|
|
Licensing and Credentialing |
Understand the licensing requirements for healthcare providers offering telemedicine services. Regulations may vary by state or country, and compliance often requires providers to hold licenses in both the patient's and provider's locations. Compliance with these licensing regulations is essential. |
|
Data Privacy and Security (HIPAA) |
In the United States, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) sets strict standards for safeguarding patient information. Ensure that your telemedicine platform complies with HIPAA regulations, especially regarding the storage, transmission, and protection of electronic patient health information. |
|
Informed Consent |
Clearly communicate the nature of telemedicine services, potential risks, benefits, and limitations to patients. Obtain informed consent from patients before providing telemedicine services to ensure they understand the nature of virtual care. |
|
Medical Licensure Compact (MLC) |
In the United States, the Interstate Medical Licensure Compact (IMLC) allows physicians to practice across state lines more easily. If your telemedicine providers operate in multiple states, compliance with the MLC may streamline the licensing process. |
|
Prescription Laws |
Familiarize yourself with prescription laws, which can vary by jurisdiction. Some states or countries have specific regulations regarding the prescription of controlled substances and telemedicine prescribing practices. |
|
Reimbursement Regulations |
Work with payers, such as insurance companies and government programs, to understand the reimbursement policies for telemedicine services. Comply with their requirements to receive reimbursement for services provided. |
|
Telehealth Parity Laws |
Many states in the U.S. have passed telehealth parity laws that mandate that telemedicine services be reimbursed at the same rate as in-person services. Ensure compliance with these laws |
When you talk about the technology infrastructure for delivery of healthcare services remotely, it implies that the platform should support secure video conferencing, messaging, file sharing, and remote monitoring, and they should integrate seamlessly with electronic health records (EHRs) and other healthcare systems. In addition, ensure that healthcare facilities and providers have access to high-speed, reliable internet connections. This is vital for conducting clear and uninterrupted virtual consultations.
Data Security and Privacy
For Data Security and Privacy, platform must Implement strong data security measures, including encryption, secure authentication, and access control, to protect patient health information. Compliance with data privacy regulations, such as HIPAA, is essential.
Secure data storage
Establish secure data storage systems and backup solutions to store patient records, consultation data, and other essential information. Regularly back up data to prevent loss during technical failures.
Backup
Establish backup systems and plans for handling technical outages or emergencies. This may include backup power sources and alternative communication methods to ensure continuity of care during disruptions.
Accessibility
Ensure that your technology infrastructure is accessible to all patients, including those with disabilities. This includes offering support for screen readers, sign language interpreters, and other accessibility tools.
Scalability
Plan for scalability to accommodate the growing demand for telemedicine services. Ensure that your technology infrastructure can expand to meet the needs of a larger patient population.
Train healthcare providers and engage patient in telemedicine protocols. This step is a critical aspect of a successful telemedicine program. It includes teaching them how to conduct virtual consultations, engage with patients remotely, and ensure the quality of care.
Ensure that providers are comfortable with the telemedicine technology you've chosen. This includes training them on how to use the telemedicine platform, schedule appointments, access patient data securely, and troubleshoot common technical issues.
Educate providers about patient data privacy and security regulations, such as HIPAA, and the importance of safeguarding patient information during telemedicine encounters.
Workflow Integration in your telemedicine program refers to the seamless incorporation of telemedicine services into existing healthcare workflows. This ensures that virtual care is efficiently delivered, coordinated with in-person care when necessary, and provides a consistent and high-quality experience for both patients and healthcare providers.
For example:
Scheduling and Appointment Management
Integrate telemedicine appointments into your scheduling system. Ensure that patients can easily book virtual visits, and that healthcare providers have a clear view of their telemedicine appointments alongside in-person ones.
EHR Integration
Ensure that your telemedicine platform seamlessly integrates with your electronic health records (EHR) system. This enables healthcare providers to access patient medical histories, document virtual consultations, and maintain a comprehensive patient record.
Billing and Reimbursement
Integrate telemedicine billing and reimbursement processes into your existing financial workflows. This includes verifying insurance coverage for telemedicine services, submitting claims, and managing payment transactions.
Security and Privacy is a fundamental aspect already covered in every key element which we have discussed earlier. So, let’s just point out the key component of this aspect here.
| Key Points | Requirements to adhere |
|---|---|
|
Data Encryption |
Implement end-to-end encryption for all telemedicine communications, including video consultations, messages, and files/data transmission. Encryption ensures that patient data is protected from unauthorized access. |
|
Access Control |
Implement strict access control measures to restrict system and data access to authorized personnel only. This includes the use of secure user authentication methods, password policies, and role-based access permissions |
|
Authentication and Authorization |
Utilize strong authentication methods, such as two-factor authentication, to verify the identity of users. Ensure that users only have access to the information and features they are authorized to use. |
|
HIPAA Compliance (or Relevant Regulations) |
Comply with healthcare privacy regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States, and other applicable data protection laws in your jurisdiction. This includes maintaining proper documentation, audits, and safeguards to protect patient data. |
|
Incident Response Plan |
Develop an incident response plan to address security breaches or data incidents. Establish procedures for reporting and managing security breaches promptly to minimize potential harm to patients. |
|
Secure EHR Integration |
Ensure that telemedicine platforms integrate securely with electronic health records (EHRs) while maintaining data privacy and security standards. Patient records should be protected during transmission and storage. |
|
Mobile Device Security |
Enforce mobile device security measures for healthcare providers who use smartphones or tablets for telemedicine consultations. This includes encryption, remote wipe capabilities, and secure app usage. |
Reimbursement Models" in telemedicine refer to the methods by which healthcare providers are compensated for the services they deliver remotely. These models vary depending on the healthcare system, payer policies, and the specific telemedicine services offered. For example:
Fee-for-Service (FFS)
In the fee-for-service model, healthcare providers are paid a set fee for each telemedicine service or consultation they provide. This model is commonly used in traditional fee-for-service healthcare systems, where reimbursement is tied to the volume of services delivered.
Capitation
Capitation is a prepaid reimbursement model where providers receive a fixed monthly payment for each patient they care for, regardless of the number of services rendered. Capitation promotes cost-effective care and can include telemedicine services in its bundled payment.
Subscription or Membership Models
Some telemedicine providers offer subscription-based or membership-based services. Patients pay a regular fee to access a range of telemedicine services, including virtual consultations, ongoing support, and education. Pay-per-visit models involve reimbursement for each telemedicine consultation or virtual visit. Providers are compensated based on the number of visits conducted, and payment is made for each individual interaction.
Similarly, there are other models such as pay-per-visit, Medicare and Medicaid Reimbursement, Commercial Insurance Reimbursement, Telemedicine Grant Programs etc.
The choice of reimbursement model can significantly impact the financial sustainability of a telemedicine program. Providers and healthcare organizations should carefully consider their specific patient population, services offered, and regulatory environment to select the most appropriate reimbursement model for their telemedicine program.
Quality assurance in telemedicine is crucial to ensure that virtual care is on par with, or even exceeds, the quality of in-person care. Essential aspects of this key point include:
Peer Reviews and Feedback
Encourage peer reviews among healthcare providers who deliver telemedicine services. Peer evaluations can help identify areas for improvement and ensure that providers maintain high clinical standards.
Patient Feedback and Satisfaction
Collect patient feedback on their telemedicine experiences. Use patient satisfaction surveys to gauge the quality of care, communication, and overall experience. Make necessary improvements based on patient input.
Data Monitoring and Analysis
Track key performance indicators (KPIs) related to patient health, outcomes, and adherence to guidelines.
Audit and Evaluation
Conduct regular audits and evaluations of telemedicine encounters to assess the adherence to clinical guidelines, documentation accuracy, and security protocols.
Technology Reliability
Ensure that telemedicine technology is reliable and capable of providing clear video and audio. Address technical issues promptly to maintain the quality of virtual care.
This aspect of telemedicine involves the development of strategies and protocols to address unexpected challenges, such as technical failures, natural disasters, or public health emergencies. Planning must ensure the continuity of care during crises, including the ability to switch between virtual and in-person care as needed.
Example: Begin by identifying the types of crises or emergencies that could disrupt telemedicine services. This could include technical outages, natural disasters, public health emergencies, cyberattacks, or other unforeseen events. Designate an emergency response team responsible for coordinating crisis management. This team should consist of key individuals with defined roles, including a crisis manager, IT support personnel, and communication coordinators.
It also encompasses communication plans, backup technology solutions, and emergency response protocols to maintain healthcare access and patient safety during unforeseen events.
Example: Implement backup technology solutions to ensure the continuity of telemedicine services during technical outages or disruptions. Develop processes for notifying patients about the crisis and rescheduling or redirecting their care.
Harnessing the true power of telemedicine requires a strategic vision aligned with organizational goals. Compliance with regulations, robust technology infrastructure, and continuous provider training are foundational. A patient-centric approach, coupled with targeted population health initiatives, underscores the inclusive nature of telemedicine. Future-proofing involves adaptability, scalability, and staying abreast of emerging technologies.
By addressing these key areas, healthcare organizations can harness the full potential of telemedicine, offering safe, effective, and convenient remote healthcare services to patients.
I trust that this article has comprehensively addressed the various background elements involved in constructing a Telemedicine Application. Addressing these factors is crucial to guarantee the efficient and secure provision of telemedicine services.
Metwaves Technologies excels in developing tailored solutions that meet the unique needs of healthcare providers and patients, ensuring seamless and secure virtual healthcare delivery. We pride ourselves on our ability to thoroughly analyze and drill down into the specifics of client's business pain points. Get-in touch with us and share your story.

